Wrist tendonitis and sprains can both result in wrist pain and affect wrist movement and strength. While these two conditions have many similarities, there are also noticeable differences in symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Most importantly, wrist tendonitis and sprain affect different types of tissues:
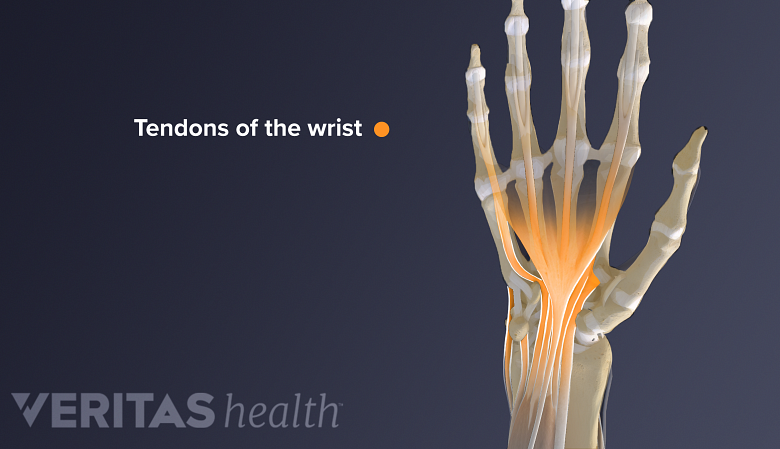
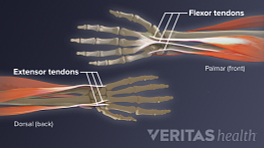
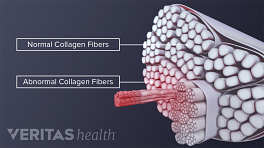
Wrist tendonitis is the inflammation due to small (micro) tears in one or more tendons of the wrist. 1 Bass E. Tendinopathy: why the difference between tendinitis and tendinosis matters. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2012;5(1):14-7.x A wrist’s tendon is a fibrous band of tissue that connects a forearm muscle to a wrist, finger, or forearm bone. Tendons of the hand muscles may also attach to the wrist bones. Tendonitis is usually caused by overuse of the tendons as opposed to a one-time injury to the tendons.
The wrist’s tendons are bundles of long fibrous bands of tissue that connect a muscle to a bone.
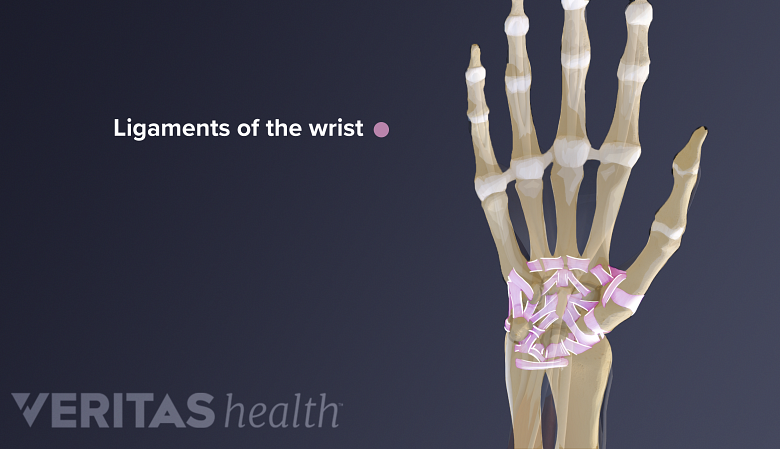
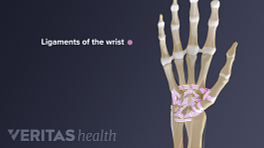
Wrist sprain is the stretching and/or tearing of one or more ligaments in the wrist. A ligament is a fibrous band of tissue that connects two bones together. In the wrist, a ligament either connects two wrist bones with each other or connects a wrist bone with a bone in the forearm or hand. Wrist sprains are usually the result of a specific injury rather than overuse.
Ligaments of the wrist are fibrous bands of tissue that connect one bone to the other.
Differences in Symptoms of Wrist Tendonitis and Sprain
Although many symptoms are similar in both wrist tendonitis and sprain, here are a few differentiating factors to help distinguish between the two conditions.
Pain
Both tendonitis and sprain cause wrist pain.
- Wrist tendonitis pain may be felt as a burning sensation, a sharp stabbing pain, or a constant dull ache. Pain may also radiate up to the elbow on the affected side.
- Wrist sprain pain may be felt as a sharp, throbbing pain or an intermittent, dull ache. The most common type of sprain (called a scapholunate ligament injury) causes pain in the center and/or thumb side of the wrist. 2 Andersson JK. Treatment of scapholunate ligament injury: Current concepts. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(9):382-393.
Movements and activities
Although any activity involving the wrist may cause pain in tendonitis and sprain, certain movements of the hand may help differentiate between the two conditions.
- Activities causing tendonitis pain include actions such as opening and closing the hand. Pushing oneself up from a chair may also cause wrist tendonitis pain. Tendonitis pain is often worsened after prolonged or repeated movements.
- Activities causing sprain pain include putting weight through the wrist particularly while bending the wrist forward and backward or during side-to-side movements. Opening a jar or turning a doorknob may also cause wrist sprain pain.
Appearance
Both, wrist ligament and tendonitis may cause warm and swollen wrists.
- Wrist tendonitis swelling may result in a swollen wrist, and may also include parts of the forearm, hand, and/or fingers.
- Wrist sprain swelling may be prominent at the wrist joint.
Effect on strength
Reduced strength in the hand and wrist are common in both tendonitis and sprain.
- Wrist tendonitis may cause difficulty with repetitive movements and in lifting and/or throwing heavy objects.
- Wrist sprains may cause decreased pinch strength and/or decreased ability to grasp an object.
Muscle symptoms
In some cases, muscles of the forearm may be affected, especially in tendon injury.
- Muscle fatigue in wrist tendonitis may cause muscle spasms or cramps in the forearm muscles.
- Muscle fatigue in wrist sprain are less common.
Both conditions may cause a general feeling of wrist weakness, reduced flexibility, and/or a feeling of painful pulling or stretching on moving the wrist joint.
Differences in Possible Causes of Wrist Tendonitis and Sprain
While tendon injuries occur due to repeated use or trauma, ligament injuries in the wrist are more likely to occur as a result of sudden, acute trauma.
- Wrist tendonitis is typically caused by repetitive motions. Activities that can lead to tendonitis include sports, such as racquet sports, and work-related activities, such as clicking the computer mouse or using a screwdriver. Tendonitis may also result from normal daily activities related to the way the hands and wrists are used in daily life.
- Wrist sprains, on the other hand, are typically caused by a specific, sudden, acute injury. Falling on an outstretched hand, playing certain sports, or motor vehicle accidents are common causes of wrist sprains. 2 Andersson JK. Treatment of scapholunate ligament injury: Current concepts. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(9):382-393. Racquet sports, rock climbing, and weight lifting are some examples of sports that may cause wrist sprains.
Initial treatments for both wrist sprain and wrist tendonitis include rest, placing an ice pack at regular intervals, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and wearing a wrist splint. If appropriately treated, both conditions should improve in days to weeks. If pain is severe or not improving with time and rest, it is important to get evaluated by a doctor to prevent the prolonged recovery or permanent damage to the wrist joint area.