A hip labral tear is a common injury that may cause hip and groin pain as well as other symptoms, such as hip locking or instability, depending on the severity and location of the tear. Labral tears are often the result of repetitive use from high impact sports or a one-time trauma. This article describes what a healthy hip labrum does, what causes a hip labral tear, symptoms, and how doctors diagnose and treat these tears.
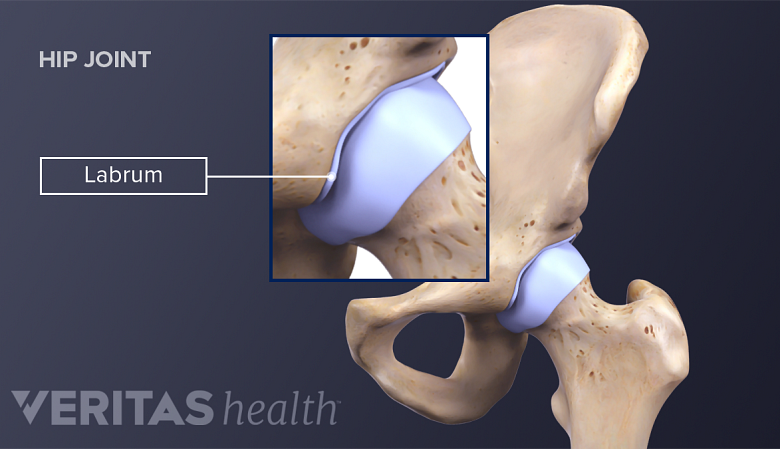
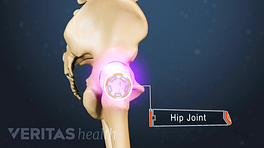
The hip labrum is a ring of cartilage surrounding the hip socket.
In This Article:
Hip Labrum Anatomy and Function
The hip labrum is a ring of strong, flexible cartilage that rims the outer edge of the hip socket (acetabulum). The labrum serves several purposes, including:
- Deepening the joint and increasing the surface area of the hip socket by 21% 1 Groh MM, Herrera J. A comprehensive review of hip labral tears. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2009;2(2):105-17.
- Allowing for a significant range of motion
- Helping maintain alignment between the hip’s ball and socket
- Keeping joint fluid inside the hip joint capsule (joint fluid reduces joint stress and friction and allows the ball and socket to smoothly move past one another)
Understanding hip anatomy is important to understanding a labral tear and its possible effects.
Types of Hip Labral Tears
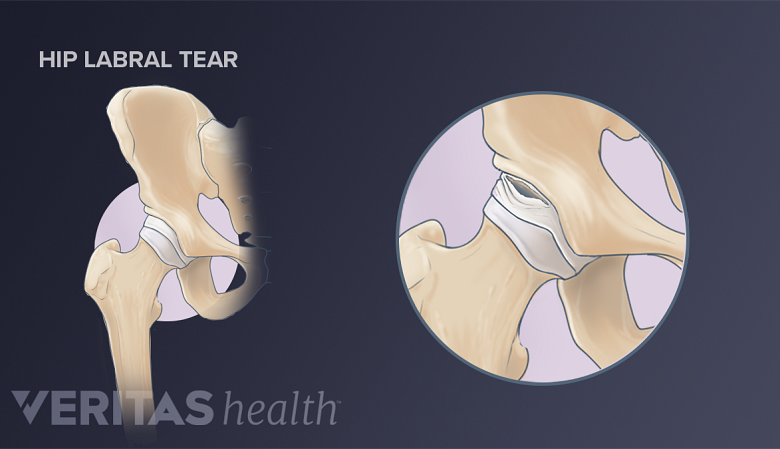
Anterior hip labral tear.
Doctors often classify hip labral tears by their location:
- Anterior labral tears, located at the front of the hip, are most common. Two contributing factors to the development of anterior tears include hip joint stress, such as repetitive pivoting, and poor vascular supply to the hip joint. 2 Martin RL, Enseki KR, Draovitch P, Trapuzzano T, Philippon MJ. Acetabular labral tears of the hip: examination and diagnostic challenges. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36(7):503-15. Studies suggest that this portion of the labrum lacks blood vessels, which makes it more susceptible to injury. 1 Groh MM, Herrera J. A comprehensive review of hip labral tears. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2009;2(2):105-17.
- Posterior labral tears, located at the back of the hip, are less common. These types of tears are associated with movements that put stress on the back of the hip joint, such as frequent squatting. 3 Robertson WJ, Kadrmas WR, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:88-92.
The underlying cause, size, and severity of a tear can vary. These differences may be noted by the doctor and can determine whether surgery is recommended. 4 Shindle MK, Voos JE, Nho SJ, Heyworth BE, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 4:2-19.
- 1 Groh MM, Herrera J. A comprehensive review of hip labral tears. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2009;2(2):105-17.
- 2 Martin RL, Enseki KR, Draovitch P, Trapuzzano T, Philippon MJ. Acetabular labral tears of the hip: examination and diagnostic challenges. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36(7):503-15.
- 3 Robertson WJ, Kadrmas WR, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:88-92.
- 4 Shindle MK, Voos JE, Nho SJ, Heyworth BE, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 4:2-19.